When you're buying a property in the UK, one of the most important financial decisions you'll make is choosing the right mortgage. Among the various types available, fixed-rate and variable-rate mortgages are the most common. Understanding the differences between them can help you select the best option for your situation.
What is a Fixed-Rate Mortgage?
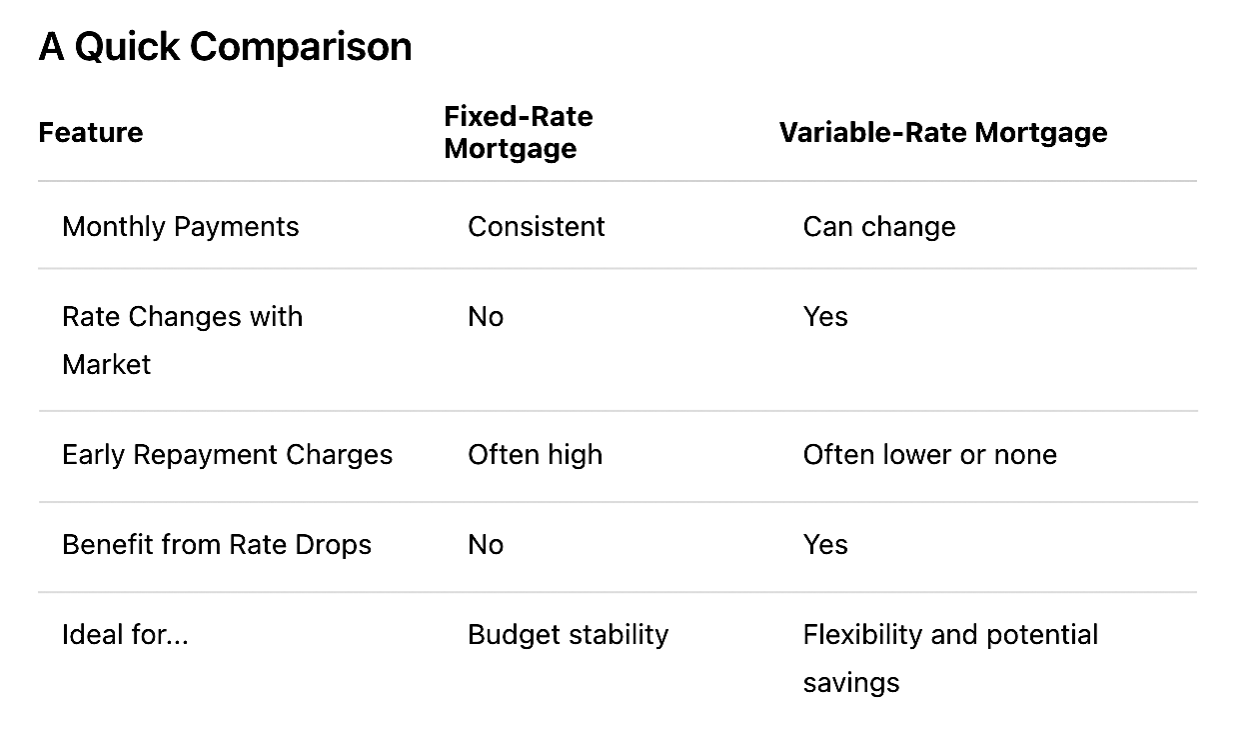
A fixed-rate mortgage means your interest rate stays the same for a set period, typically between 2 and 10 years. During this time, your monthly repayments won’t change, regardless of fluctuations in the Bank of England base rate or wider market conditions.
Advantages:
- Predictability: Your monthly payments stay the same, making it easier to budget.
- Protection from Rate Rises: If interest rates go up, your mortgage rate won’t be affected.
- Peace of Mind: You won’t face surprise increases in your monthly repayments.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of Flexibility: You won’t benefit if interest rates fall.
- Early Repayment Charges (ERCs): If you want to switch deals or repay your mortgage early during the fixed term, you may face significant fees.
- Potentially Higher Initial Rate: Fixed-rate deals may start higher than some variable options.
What is a Variable-Rate Mortgage?
A variable-rate mortgage means your interest rate can change over time. These changes are usually linked to the Bank of England base rate or your lender’s own standard variable rate (SVR).
Types of Variable-Rate Mortgages:
- Standard Variable Rate (SVR): Set by your lender, this rate can change at any time.
- Tracker Mortgage: Tracks the Bank of England base rate plus a set percentage.
- Discounted Variable Rate: Offers a discount off the lender’s SVR for a limited time.
Advantages:
- Potential for Lower Rates: If interest rates fall, your payments could decrease.
- More Flexibility: Many variable mortgages have lower or no early repayment charges.
- Opportunity to Overpay: Some allow you to pay off your mortgage faster without penalties.
Disadvantages:
- Uncertainty: Your monthly payments can increase if interest rates rise.
- Harder to Budget: With rates fluctuating, managing monthly finances can be trickier.
- Market Dependency: You’re more exposed to economic changes.
Key Factors to Consider
When deciding between fixed and variable mortgage rates in the UK, think about:
- Current Interest Rate Trends: If rates are low but expected to rise, a fixed-rate deal might offer security.
- Your Financial Stability: If your income is steady and you can handle fluctuations, a variable rate might save money.
- Length of Stay in the Property: If you plan to move soon, a variable rate with low ERCs could be more cost-effective.
- Risk Tolerance: Do you prefer stability, or are you comfortable with some financial unpredictability?
Final Thoughts
There is no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to choosing a mortgage. Fixed-rate mortgages provide security and peace of mind, while variable-rate options offer flexibility and the possibility of savings. Your decision should depend on your financial goals, market outlook, and personal comfort with risk.
Before committing, always consult a qualified mortgage advisor and property expert who can assess your situation and recommend the most suitable product. We have over a decade of experience in this industry and can help refer you to experts that can save you thousands over the life of your mortgage—so get in contact today!
0121 681 6327